Prenatal Care: The Importance Of Regular Checkup And Screening
Prenatal care plays a crucial role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. It involves a series of medical checkups, screenings, and guidance provided by healthcare professionals throughout pregnancy.
Regular prenatal care not only helps in monitoring the progress of the pregnancy but also enables early detection and management of any potential complications. In this article, we will explore the significance of prenatal care, the benefits it offers, and when to seek medical attention during pregnancy.
Bringing a new life into the world is a momentous journey, and prenatal care acts as a compass that guides expectant mothers through this transformative process. It encompasses various aspects of healthcare, including medical examinations, tests, vaccinations, nutritional advice, and emotional support.
Prenatal care is typically initiated as soon as a woman discovers she is pregnant and continues until delivery, ensuring that both mother and baby receive the necessary care and support.
Did you know that the World Health Organization reports that approximately 830 women lose their lives every day due to preventable causes associated with pregnancy and childbirth? This staggering statistic highlights the urgent need for proper prenatal care.
The lack of access to quality prenatal care significantly increases the risk of complications and adverse outcomes for both the mother and the baby. However, by prioritizing regular checkups and screenings, expectant mothers can significantly reduce these risks and enhance the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
The Benefits of Regular Prenatal Care : Checkups
⦁ Early detection of potential complications:
1. Helps identify any problems early on, allowing for timely treatment and management.
2. Reduces the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
⦁ Monitoring the baby’s growth and development:
1. Allows healthcare providers to track the baby’s growth through regular measurements and ultrasounds.
2. Ensures that the baby is developing properly and identifies any concerns that need attention.
⦁ Screening for health conditions:
1. Routine screenings and tests can detect health conditions that may affect the mother or the baby.
2. Helps identify issues such as diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and genetic abnormalities.
⦁ Nutritional guidance and advice:
1. Healthcare providers offer guidance on maintaining a healthy diet and getting the necessary nutrients during pregnancy.
2. Ensures that the mother and the baby receive proper nutrition for their well-being.
⦁ Monitoring maternal health:
1. Regular checkups allow healthcare providers to assess the mother’s overall health and well-being.
2. Helps manage any health concerns or complications that may arise during pregnancy.
⦁ Emotional support and counseling:
1. Prenatal checkups provide an opportunity for expectant mothers to discuss their emotions and concerns.
2. Offers emotional support and guidance to help cope with the physical and emotional changes of pregnancy.
⦁ Education and preparation for childbirth:
1. Prenatal care provides valuable information on childbirth, breastfeeding, and postpartum care.
2. Helps expectant mothers feel prepared and confident in their journey towards motherhood.
⦁ Building a relationship with healthcare providers:
1. Regular checkups allow expectant mothers to develop a relationship with their healthcare providers.
2. Builds trust, promotes open communication, and ensures personalized care throughout the pregnancy.
⦁ Enhanced overall pregnancy experience:
1. Regular checkups provide reassurance and peace of mind for expectant mothers.
2. Offers a sense of security knowing that both mother and baby are being closely monitored and cared for.
⦁ Reduced maternal and neonatal mortality:
1. Adequate prenatal care significantly reduces the risk of maternal and neonatal mortality.
2. Detecting and managing complications early leads to safer pregnancies and childbirth.
By attending regular prenatal checkups, expectant mothers can benefit from early detection of complications, monitoring the baby’s growth, receiving necessary screenings, obtaining nutritional guidance, emotional support, and education. Prenatal care not only improves the pregnancy experience but also promotes the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Prenatal Care : Screening
Advantage
1. Early detection and management of complications.
2. Reduced risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
3. Improved maternal and fetal health.
4. Nutritional guidance for a healthy pregnancy.
5. Emotional support and education for expectant mothers.
Disadvantage
1. Cost and accessibility barriers in some regions.
2. Time-consuming nature of frequent checkups.
3. Invasive tests and procedures may cause anxiety for some women.
4. Overmedicalization and potential for unnecessary interventions.
Treatment at the Doctor’s Office:
Here’s an overview of the treatments and interventions that may occur during prenatal checkups and screenings, organized by each month of pregnancy:
First Trimester (Months 1-3) Prenatal Care
Initial prenatal visit:
1. Confirming the pregnancy through a urine or blood test.
2. Establishing a comprehensive medical history.
Blood tests:
1. Checking blood type and Rh factor.
2. Screening for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
3. Testing for immunity to certain diseases like rubella and chickenpox.
Urine tests:
1. Assessing kidney function.
2. Detecting any signs of urinary tract infections.
Physical examination:
1. Measuring blood pressure and weight.
2. Checking for signs of swelling or preeclampsia.
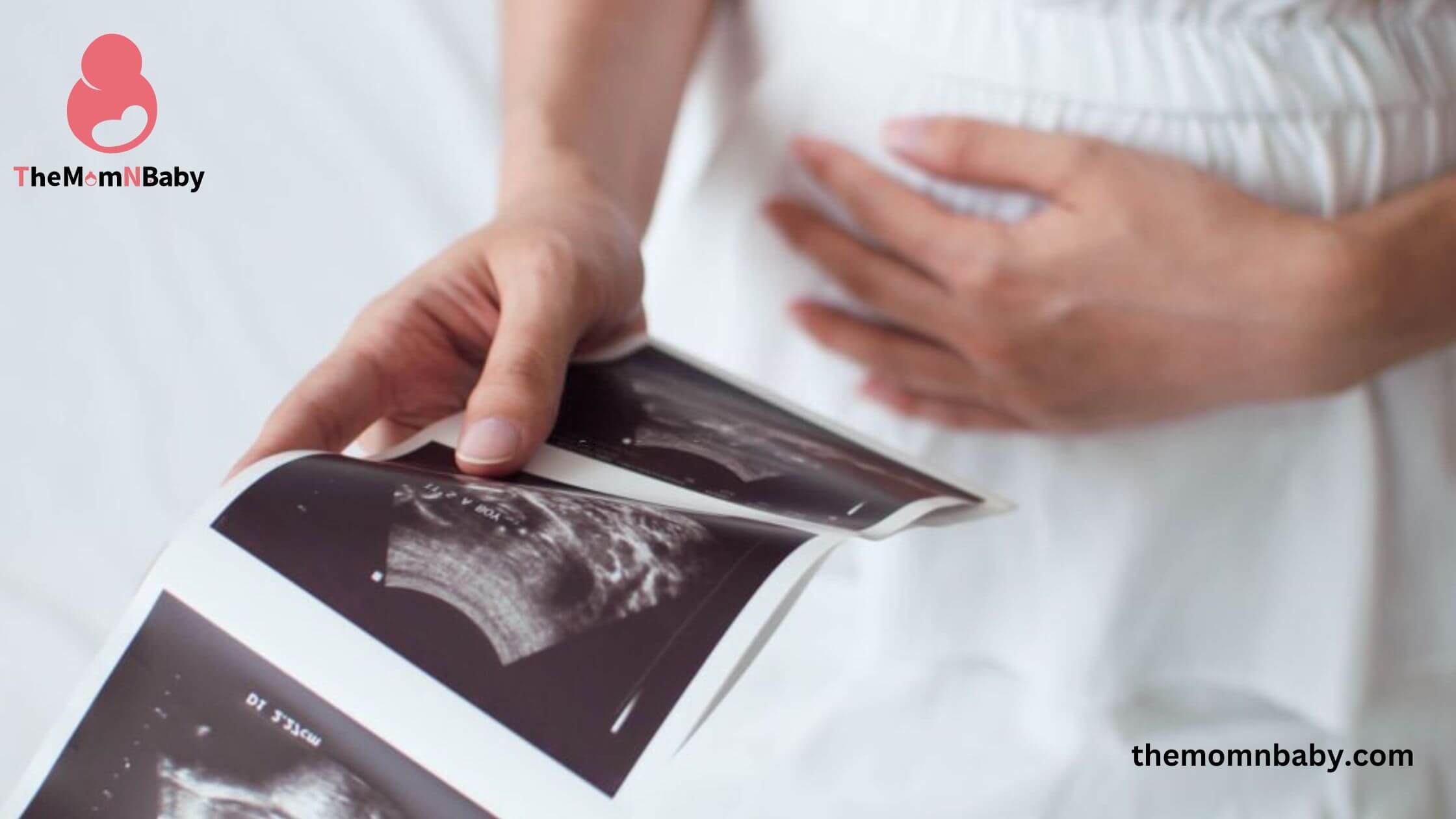
Ultrasound:
1. Confirming the gestational age and due date.
2. Assessing the number of embryos/fetuses.
3. Detecting the baby’s heartbeat.
Nutritional guidance:
1. Discussing dietary requirements and prenatal vitamins.
2. Advising on managing morning sickness and food aversions.
Second Trimester (Months 4-6) Prenatal Care
Routine checkups:
1. Monitoring blood pressure, weight, and urine.
2. Assessing the size and position of the uterus.
3. Listening to the baby’s heartbeat.
Blood tests:
1. Screening for gestational diabetes.
2. Checking iron levels and anemia.
Ultrasound:
1. Assessing fetal growth and development.
2. Examining fetal anatomy and detecting any abnormalities.
Genetic testing:
1. Offering optional screenings for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
2. Conducting tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling if necessary.
Rh factor testing:
1. Determining if the mother’s blood is Rh-negative and if Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) injections are needed.
Nutritional guidance:
1. Discussing a balanced diet and appropriate weight gain.
2. Addressing common discomforts like heartburn or constipation.
Third Trimester (Months 7-9) Prenatal Care
Regular checkups:
1. Monitoring blood pressure, weight, and urine.
2. Assessing fetal growth, position, and movement.
3. Monitoring the mother’s well-being and signs of preeclampsia.
Glucose screening:
1. Conducting a glucose tolerance test to diagnose gestational diabetes if necessary.
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening:
1. Collecting a swab to check for GBS bacteria that could affect the baby during delivery.
Non-stress test (NST) or biophysical profile (BPP):
1. Assessing fetal heart rate and movement to ensure the baby’s well-being.
Pelvic exams:
1. Checking the cervix for dilation and effacement as the due date approaches.
Breastfeeding preparation:
1. Discussing breastfeeding techniques and addressing any concerns or questions.
It’s important to note that the specific treatments and interventions may vary depending on individual circumstances and healthcare providers’ protocols. Prenatal care is tailored to meet the unique needs of each expectant mother, and healthcare providers will determine the appropriate interventions and screenings based on the stage of pregnancy and any specific risk factors.
When to Call a Doctor:
While routine prenatal checkups are essential, there are instances when expectant mothers should reach out to their healthcare providers between scheduled appointments. Some situations that warrant immediate medical attention include:
1. Vaginal bleeding or spotting.
2. Severe abdominal pain or cramping.
3. Decreased fetal movement.
4. Persistent headaches or visual disturbances.
5. Signs of preterm labor, such as regular contractions before 37 weeks.
6. Leakage of amniotic fluid.
7. Sudden swelling of the face, hands, or legs.
Prenatal care is a vital component of a healthy pregnancy, benefiting both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. Regular checkups and screenings facilitate early detection and management of potential complications, ensuring better outcomes for both mother and baby. Additionally, prenatal care provides crucial guidance, emotional support, and education to expectant mothers, promoting their overall well-being.
By prioritizing prenatal care, we can significantly reduce the risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth and pave the way for a healthy start to parenthood. Here we discuss about most asked questions about screening and check-up.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How often should I schedule prenatal checkups?
A: In general, prenatal checkups are recommended once a month during the first and second trimesters, every two weeks from week 28 to week 36, and then weekly until delivery. However, the frequency may vary based on individual circumstances, so it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider.
Q: What tests are typically performed during prenatal care?
A: Common tests during prenatal care include blood tests to check for anemia, infections, and genetic abnormalities, urine tests to monitor kidney function and detect urinary tract infections, and ultrasounds to assess fetal development and anatomy.
Q: Is prenatal care only for first-time mothers?
A: No, prenatal care is essential for all pregnant women, regardless of whether it’s their first pregnancy or subsequent ones. Each pregnancy is unique and requires appropriate monitoring and care to ensure a healthy outcome.
Q: Can I continue taking my regular medications during pregnancy?
A: It is important to consult with your healthcare provider about any medications you are currently taking. Some medications may need to be adjusted or discontinued during pregnancy, while others are safe to continue. Contact your Doctor for specific medicine.
Q: What if I don’t have access to prenatal care due to financial constraints?
A: Many countries offer government-funded healthcare programs or low-cost clinics specifically for prenatal care. Additionally, community organizations and nonprofit groups often provide assistance to expectant mothers in need. Reach out to local resources to explore available options for affordable or free prenatal care.